Up to 20% of all people over the age of 25 are at risk of developing deforming knee osteoarthritis. The knee joint works in axial compression mode, therefore its articular surfaces are subjected to constant loads and are subject to degenerative changes in hyaline cartilage.
%20and%20affected%20by%20osteoarthritis%20(left).jpg)
frequency
The pathology of the articular cartilage of a degenerative-dystrophic nature with the participation of bone tissue, articular bag, ligaments and muscles is called deforming arthrosis. In the terminology there are synonyms:
- Arthrosis;
- Arthrosis;
- degenerative arthritis;
- Arthrosis;
- hypertrophic arthritis;
In terms of frequency, the damage to the knee comes immediately after the hip joint, so that a fixed term has been formed: "gonarthrosis of the knee joint". The dependence of the frequency of the disease on age was examined:
| 26 - 44 years old | 5% of adults |
| 45 - 59 years old | 16, 70% |
| 60-69 years old | 12, 10% |
| 70 years and older | eleven% |
In all age groups, representatives of the fairer sex quantitatively predominate. In them, arthrosis of the knee occurs 1, 2-1, 4 times more often than in men.
In the area of permanent disabilities, deforming arthrosis of the knee joint accounts for almost 30% of all causes of disabilities related to joint pathologies.
Classification of gonarthrosis
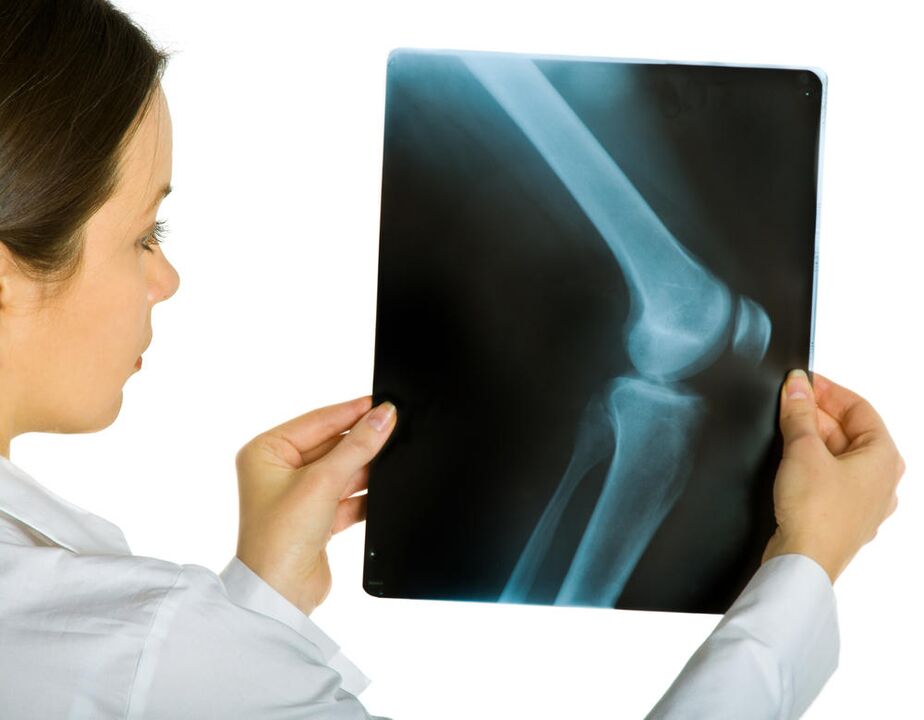
For reasons of development, the disease is divided into two large groups: primary and secondary. The primary arises without visible prerequisites. The secondary is preceded (or accompanied) by provocative factors:
- biomechanical disorders: injuries, excessive loads, developmental anomalies (dysplasia), skeletal pathology (scoliosis, flat feet), obesity;
- inflammatory processes: aseptic or infectious arthritis, frequent hemarthrosis in hemophilia;
- Metabolic diseases: gout, hemochromatosis, Paget's disease;
- Endocrine disorders: acromegaly, diabetes mellitus, parathyroid disorders;
- Violations of adequate blood supply: varicose veins and postthrombophlebitic syndrome, obliterating endarteritis, atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities;
In medical practice, a classification according to the severity of pathological changes makes more sense. The assessment is based on X-ray examinations. The most popular clinical and radiological classification.
I direct
The picture shows a slight narrowing of the joint space (compared to a healthy joint), incipient sclerosis of the pericartilaginous bone tissue. Clinical - pain occurs when walking or immediately after standing for a long time. More pronounced when climbing stairs. Happens in peace. First-degree gonarthrosis does not significantly affect the function of the joint.
Stage II
The joint space is 2-3 times narrower than normal. Sclerosis is more pronounced, osteophytes are found (prickly growths of bone tissue along the edges of the joint space and condyles). The pain is moderate, there are signs of muscle hypotrophy, lameness. The deformation of the knee in the frontal axis is visible. Second-degree gonarthrosis leads to a noticeable restriction in joint mobility.
III. stage
Sclerosis of cartilaginous elements, deformation of articular surfaces. There are areas of subchondral necrosis, local osteoporosis. Cysts in adjacent bone tissue. The joint space is critically narrowed, sometimes undefined. Osteophytes of considerable size. Atrophy of the thigh and lower leg muscles, the joint is unstable, there is a pronounced deformity. Movement in the knee is sometimes impossible, a contracture is formed. When moving - severe pain, lameness.
This classification approach is convenient in that it allows assessment of clinical manifestations related to organic changes. It provides an opportunity to choose more effective treatment based on a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the joint.
development mechanism
The pathogenesis of any arthrosis goes through three stages:
- Damage to the microstructures of the cartilage. Under the influence of one of the harmful factors, high-molecular compounds lose their strength and become enriched with water molecules. The ability of low molecular weight collagens to assemble into macromolecules is impaired. This leads to a decrease in the strength and durability of hyaline cartilage. Chondroprotectors counteract such phenomena.
- If the provoking factor is not eliminated, the weakening of the cartilage components (glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans) continues. This leads to the activation of recovery processes. Their power reserve isn't particularly large, so this stage quickly transitions to the next.
- Disruption of the compensatory mechanisms leads to progressive destruction of articular cartilage and the death of its cells - chondrocytes. Cartilage tears extend to the underlying bone. The degree of detachment of the cartilage components increases, their fibrillation occurs, which leads to thinning of the hyaline membrane.
On the side of the bone, with deforming arthrosis of the knee joint, thickening (sclerosis) occurs, cysts and areas of uneven bone density appear. Therefore, the deformation of the articular surfaces, the instability of the joint develops.
diagnosis
The diagnosis is based on a set of data obtained as a result of questioning (anamnesis), medical examination and instrumental research methods. The latter include X-ray studies (CT, MRI), radioisotopes (scintigraphy), arthroscopy.
Objective examination
It includes the clarification of the life history of the patient, the circumstances that preceded the development of gonarthrosis of the knee joint, collection of complaints and examination. In the process, the presence of provoking factors and the degree of their influence on the development of the disease are clarified.
It is important at this stage to find out the condition of the second knee. If you overlook bilateral knee osteoarthritis and only focus on the knee that worries you more, you may be making a gross diagnostic error.
For this purpose, functional tests should be carried out on two limbs at the same time. Pain during active and passive movements, tenderness to palpation, crepitation (crunching) during extension and flexion are noted. Chronic inflammatory processes lead to the occurrence of a Becker cyst - a protrusion of the joint bag into the hollow of the knee, which can also be detected by palpation.
instrumental methods
The first is radiography. A radiograph of the knee joint in two projections allows a preliminary assessment of the condition of the joint and determination of the stage of the disease. The disadvantage of the method is that radiological signs appear later than the symptoms and morphological changes that accompany osteoarthritis of the knee joint.
In such cases, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) helps. It is possible to determine the initial stages of degenerative changes in cartilage and bone structures, it is possible to assess the condition of the intra-articular ligaments, menisci. Scintigraphy in gonarthrosis of the knee joint provides information about the functional status.
With arthroscopy, a direct examination of the joint cavity is possible.
The American College of Rheumatology proposed the following criteria for standardizing diagnostic data:
- Age over 50 years.
- Stiffness in the joint in the morning lasting at least half an hour.
- Cracking, caused by movement (active and passive).
If these symptoms are accompanied by osteophytes found on x-ray and pain, then gonarthrosis of the knee joint is very likely to occur.
The initial stages of the disease may not be pronounced, therefore, differential diagnostics is required with other joint pathologies in which drugs pathogenic for osteoarthritis (chondroprotectors) are ineffective.
All possible measures should be taken so as not to confuse gonarthrosis with the following diseases:
Rheumatoid arthritis |
Onset at an early age, morning stiffness for more than 30 minutes, pain worse at rest and less when moving, rheumatoid nodules on the skin, concomitant lesions of internal organs, signs of intoxication (fever, sweating), C-reactive protein in blood tests. |
crystal arthritis |
The pain is sharp at night or in the morning; the skin over the diseased joint is edematous, red, hot; Crystals on a microscopic examination of the synovial fluid, an increase in the level of uric acid in the blood (in gout). |
spondyloarthropathies |
Arthritis of other, unrelated joints (intercostal, lumbar joint); inflammatory processes in the tendons; Damage to cornea, skin, mucous membranes. |
In the tenth revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD 10), all these diseases are given the index "M", but a different numerical code.
These are fundamentally different pathological processes that require a professional approach to diagnosis and qualified treatment.
therapeutic measures
If there is a disease, there must be ways to heal arthrosis of the knee joint. And there they are. Help can be given in many ways.
In the first place are the achievements of traditional medicine, which are based on a thorough study of the causes and mechanisms of the disease. Medical and surgical methods are used here. Competent treatment requires the consistent and complex use of drugs, physiotherapeutic methods and rehabilitation measures.
The second way is treatment with folk remedies. The effectiveness of these methods is questionable, to say the least. But they are used because it is possible to reduce the manifestations of the disease at home. Folk remedies can only be used as an adjunct to drug treatment or as part of complex therapy, it is imperative to obtain the consent of the attending physician!
medical help
This type of treatment involves the use of various medications. For medicinal effects, drugs from different groups are used:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, opiates;
- slow-acting symptomatic drugs (chondroprotectors);
- glucocorticoid hormones;
NSAIDs, rapid analgesics, opiates
Medicines of this group are designed to eliminate pain. Pain syndrome quite spoils the life of patients with arthrosis, its removal significantly improves the quality of life of a person. NSAIDs, anilides, non-narcotic and narcotic analgesics are capable of this.
A common disadvantage is the side effects. These drugs affect the kidneys, the protective mechanisms of the gastrointestinal tract. An alternative that can reduce harmful manifestations are injections. Intramuscular administration causes less damage to the stomach and accelerates the effect.
Due to side effects, drugs of this group are prescribed during exacerbations, careful dose selection is required.
The main advantage of NSAIDs is the many forms for local treatment (ointments, gels). Allows you to control the manifestations of the disease at home.
Analgesics with a central effect are prescribed for a short time, with the other two groups being ineffective. The most popular opiate is prescribed during an exacerbation, more often with bilateral gonarthrosis. These drugs are addictive. You can't take them alone!
Symptomatic slow-acting drugs
The action of these substances is two-fold: they have the ability to relieve pain (as NSAIDs) and help restore hyaline cartilage. They are often called chondroprotectors.
The effect develops over several weeks (2-8) and lasts for 2-3 months after stopping.
In addition to chondroitin sulfate and glycosaminoglycans, this group includes preparations based on hyaluronic acid, compounds derived from avocado and soy.
The most studied and popular chondroprotectors (chondroitin sulfate and glycosaminoglycans) are ready-made components of articular cartilage. Well absorbed into the blood, high concentrations form in the joint cavity. To speed up the effect, injections can be made directly into the joint.
It has been proven that chondroitin sulfate, taken as a cure for two years in a daily dose of 800 mg, has a stabilizing effect on the joint space in the case of second-degree gonarthrosis of the knee joint.
Avocado/soy compounds have anti-inflammatory properties. By inhibiting collagenase (a breakdown enzyme), they slow down the destruction of cartilage considerably and increase the synthesis of "their" collagen. They are also very well tolerated.
Hyaluronic acid derivatives are used in the form of intra-articular injections. These funds, like chondroprotectors, improve the functional state of the knee joint.
The mechanism of action of various drugs with a slow symptomatic effect is somewhat different, so their combined use is recommended. A high level of safety allows you to take chondroprotectors for a long time without noticeable harm to the body.
glucocorticosteroids
The main effect is anti-inflammatory. These funds are prescribed when NSAIDs are ineffective. Tablet forms also damage the gastric mucosa. There are forms for intra-articular injections.
They have numerous side effects, so you should not abuse hormonal drugs for deforming arthrosis of the knee joint.
group name |
advantages |
defects |
|---|---|---|
NSAIDs, analgesics, opiates |
Fast acting, many forms for topical application. |
Side effects, unstable effect, dangerous for age-related patients, addiction occurs. |
chondroprotectors |
They have a pathogenetic effect, have a lasting effect, are non-toxic, there are forms for external and intra-articular use. |
Slow unfolding of the effect. |
hormones |
Fast acting when NSAIDs are not enough; Forms for intra-articular administration. |
Side effects, unstable effect, long-term use is impossible. |
ethnoscience

At home, you can reduce the manifestations of the disease using folk remedies. There are many recipes, but there are a few, but:
- no clinical studies have been conducted;
- it is impossible to accurately dose the drug;
- Indications are not clearly defined;
- individual tolerability of folk remedies is not taken into account;
The advantages include a wide therapeutic spectrum, a wide choice for external use. Homemade compresses and tinctures, ointments are popular.
The effectiveness of home treatment can be evidenced by the fact that biologically active substances (gum, bile, infusions of medicinal plants) are used for its preparation.
In addition, competent treatment with folk remedies begins with compliance with a diet, weight loss. This method alone, which aims to reduce the load on the joint, can reverse first-degree arthrosis of the knee joint (prerequisite is young age, sufficient ability to compensate). Healthy eating in itself stimulates the body's regenerative abilities. The diet includes: slight feeling of hunger, vegetables, freshly squeezed juices. It is advisable to add low-fat jellies and jellies to the diet.
External means are very diverse. Above all, they have an irritating and warming effect. The most studied components are bile, dimethyl sulfoxide and bischophite. Bile should be used medicinally and not extracted independently from an animal's corpse. Dimethyl sulfoxide is an analogue of a chemical warfare agent, mustard gas. Bischofite is a derivative of oil. That's the difference in origin.
All three drugs have anti-inflammatory effects, but should only be used at home after consulting a doctor. These substances also have contraindications and features of use.
We must not forget about the placebo effect in the treatment of folk remedies.
The last thing I want to convey is that a person has health. You should not completely rely on the apparent simplicity and cheapness of folk remedies. If you've already decided to try them, increase your awareness of the sore joint. The course of the disease against the background of treatment with folk remedies is a reason to reconsider the approach to therapy.
If osteoarthritis of the knee joint is diagnosed as grade 2 or higher, it is better not to bother with conventional medicine. Or postpone it for a period of remission. Inadequate treatment is an indication for complex surgical intervention.